PWG-GliadinPWG-gliadin is a reference material that has been produced under the guidance of the Prolamin Working Group (PWG). Its isolation and characterization is described in detail in van Eckert et al. (2006). Briefly, PWG-gliadin has been extracted from a mixture of 28 European wheat cultivars. Albumins and globulins were eliminated by extraction using 0.4 M NaCl solution and gliadins were extracted with 60% ethanol. The gliadin extracts were concentrated, desalted by ultrafiltration, freeze-dried, and homogenized. The residual material after lyophilization is referred to as PWG-gliadin. In 2005 PWG-gliadin was handed over to the Institute for Reference Material and Measurements of the European Commission (IRMM), Geel, Belgium to getting approved as a certified reference material. IRMM decided that PWG-gliadin would not be approved and returned it to PWG in 2006. Information on its composition is provided in the following sections.
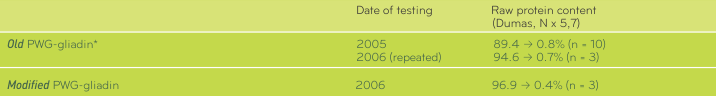
Specifications of PWG-GliadinDuring evaluation at IRMM PWG-gliadin (“Old”) was extensively dried. The material that was obtained and that is available to date is designated “Modified” PWG-gliadin in the specifications. The protein content of PWG gliadin was determined repeatedly in 2005 and 2006.Results are shown in Table 1. It can be assumed that residual acetic acid was removed during storage or by modifying. When using PWG-gliadin please note that the protein content is subject to change depending on the storage conditions and use the current protein content given in the accompanying information.
TABLE 1. Protein content of PWG-gliadin Van Eckert R, et al. Towards a new gliadin reference material – isolation and characterisation. J Cer Sci 2006; 43: 331-341.
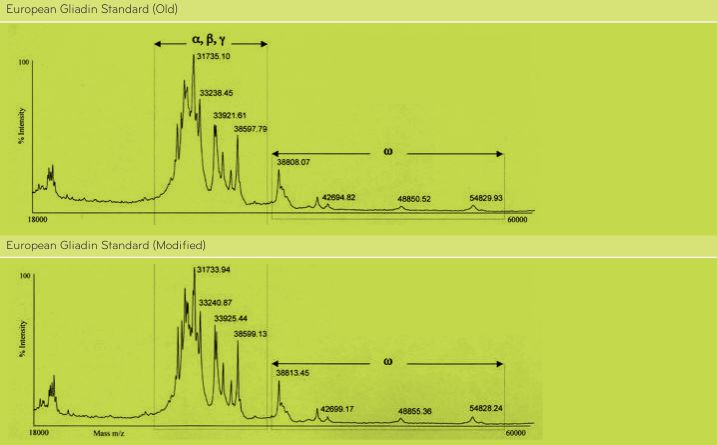
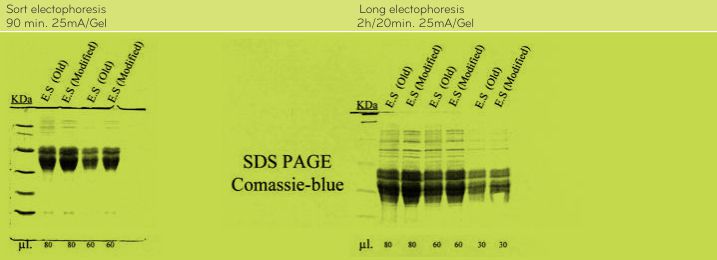
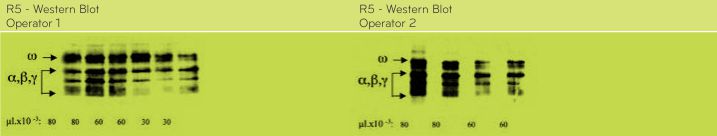
According to the analysis performed by Dr. Enrique Méndez, CSIC, Madrid, Spain, results by SDS-PAGE, R5 Western blot and MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry do not show differences between the OldPWG-gliadin and ModifiedPWG-gliadin (See Figs. 1-5, Tables 2 and 3). FIGURE 1. Analysis of PWG-gliadin (Old and Modified) by MALDI-TOF-MS.
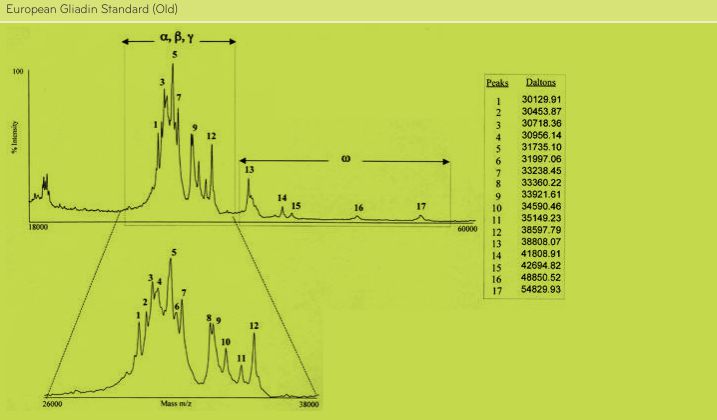
FIGURE 2. Analysis of PWG-gliadin (Old) by MALDI-TOF-MS.
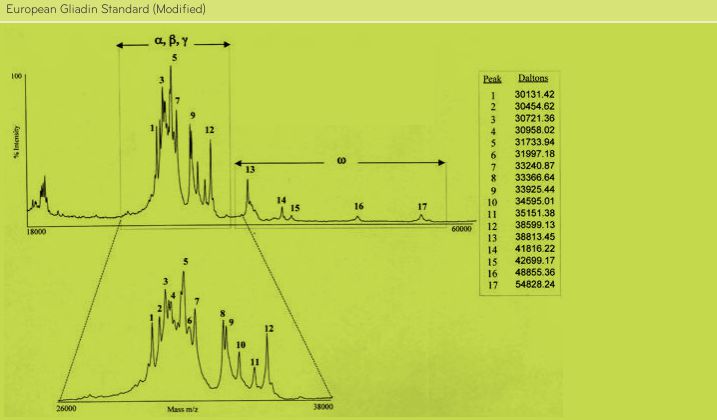
FIGURE 3. Analysis of PWG-gliadin (Modified) by MALDI-TOF-MS.
FIGURE 4. Analysis of Old and ModifiedPWG-gliadin(E.S.) by SDS-PAGE and staining with comassie-blue.
FIGURE 5. Analysis of Old and ModifiedPWG-gliadin by SDS-PAGE followed by Western-blotting and detection by immunostaining using the R5 antibody.
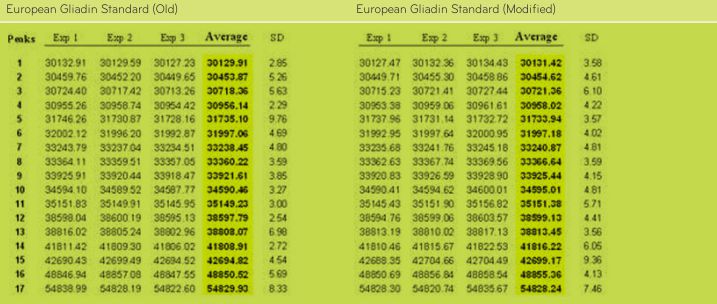
TABLE 2. Analysis of PWG-gliadin (Old and Modified) by MALDI-TOF/MS
Old and ModifiedPWG-gliadinwere analyzed three times (Exp 1, Exp 2 and Exp 3) by MALDI-TOF-MS. Average values of mass signals and standard deviations are displayed.
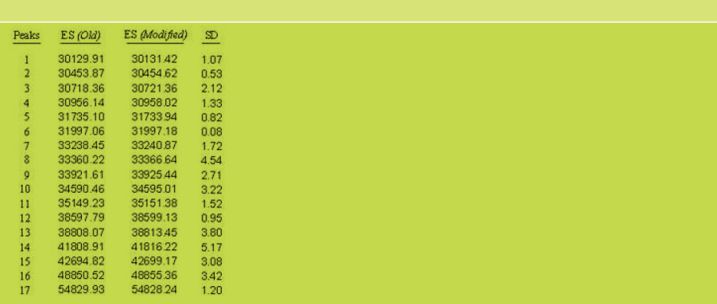
TABLE 3. Average values of mass signals obtained from MALDI-TOF-MS analysis of Old and ModifiedPWG-gliadin (ES).
|
- García E, Llorente M, Hernando A, Kieffer R, Wieser H, Méndez E. Development of a general procedure for complete extraction of gliadins for heat processed and unheated foods. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2005; 17: 529-539.- Méndez E, Llorente M, García E, Vela C, Immer U, Janssen FW. Report of a collaborative trial to investigate the performance of the R5 enzyme-linked immuno assay to determine gliadin and gluten-free food. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2005; 17: 1053-1063.- Stern M, Ciclitira P, van Eckert R, Feighery C, Janssen FW, Mendez E, Mothes T, Troncone R, Wieser H. Analysis and clinical effects of gluten in coeliac disease. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2001; 13: 741-747.- Stern M. Current Therapy. In: Fasano A, Troncone R, Branski D (eds). Frontiers in Celiac Disease. Pediatric Adolesc Med. Basel: Karger 2008; 12: 114-122.- Valdés I, García E, Llorente M, Méndez E. Innovative approach to low-level gluten determination in foods using a novel sandwich ELISA protocol. Eur J Gastroenterol 2003; 15: 465-474.- Van Eckert R, Berghofer E, Ciclitira PJ, Chirdo F, Denery-Papini S, Ellis HJ, Ferranti P, Goodwin P, Immer U, Mamone G, Méndez E, Mothes T, Novalin S, Osman A, Rumbo M, Stern M, Thorell L, Whim - A, Wieser H. Towards a new gliadin reference material - isolation and characterisation. J Cer Sci 2006; 43: 331-341.- Wieser H, Koehler P. The biochemical basis of celiac disease. Cer Chem 2008; 85: 1-13.- Gessendorfer B, Koehler P, Wieser H. Preparation and characterization of enzymatically hydrolyzed prolamins from wheat, rye, and barley as references for the immunochemical quantitation of partially hydrolyzed gluten. Anal Bioanal Chem 2009; 395:1721-1728- Gessendorfer B, Wieser H, Koehler P. Optimisation of a solvent for the complete extraction of prolamins from heated foods. J Cereal Sci. 2010; 52: 331-332
|